BED ROCK MAPPING
|
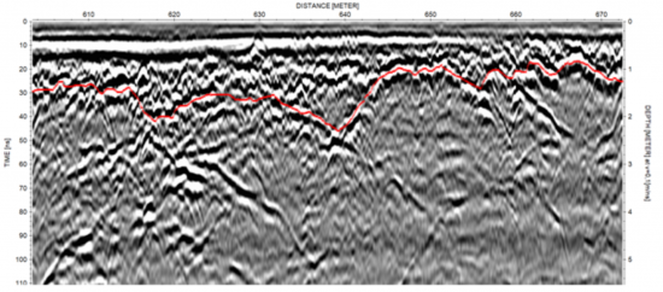
Bedrock is the hard, solid rock most often found beneath the unconsolidated surface materials, such as sand or till, but also as outcrops above the ground surface. The depth to the rock head can vary from zero to several hundred meters and the topography, as well as the quality, of the bedrock can differ significantly.
An understanding of the bedrock is important for many aspects of human activities on Earth. Knowledge of the depth to the bedrock and its properties are essential for:
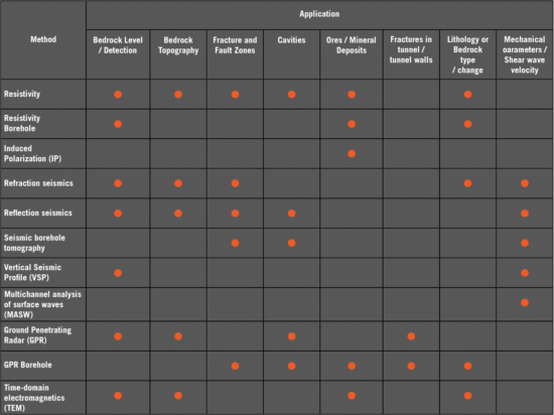
Today, most bedrock investigation is done by digging or drilling but with the increased use of 3D design tools (on infrastructure and resource mapping projects, for example) the demand for more data coverage is increasing. Attempting to resolve this need with traditional intrusive methods will be extremely expensive and sometimes, with an increasingly ‘crowded’ subsurface, digging and drilling can be most undesirable and risky. Instead, different geophysical tools can be used to assist in the creation of a more comprehensive picture of the bedrock conditions. WHich Technique?What method and technique to use? Whilst there are many factors involved in deciding upon the correct solution for a given project, these are some of the key considerations:
It is often beneficial to combine different geophysical methods to get the best resulting picture of the bedrock conditions due to the overburden conditions, the physical distribution of the bedrock or level of information required. For instance:
|
REQUEST MORE INFO
|